Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, resulting in swelling and discomfort. It usually affects the arms or legs but can occur in other parts of the body as well. This article provides insights into lymphedema and focuses on managing the associated swelling. Find the best lymphedema treatment for you with a quick search.
Causes and Risk Factors
Lymphedema typically occurs due to damage or removal of lymph nodes or lymph vessels. Common causes include cancer treatments, surgery, radiation therapy, infection, trauma, or genetic disorders. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective management.
Stages of Lymphedema
Lymphedema is categorized into stages based on the severity of swelling and symptoms. Stage 0 is a latent or subclinical stage where swelling is not evident, but impaired lymph transport exists. Stages I, II, and III indicate progressive swelling and severity of the condition, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention.
Symptoms and Complications
The primary symptom of lymphedema is persistent swelling, which may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb. Other symptoms include limited flexibility, discomfort, recurring infections, and hardening or thickening of the skin. If left untreated, lymphedema can lead to serious complications.
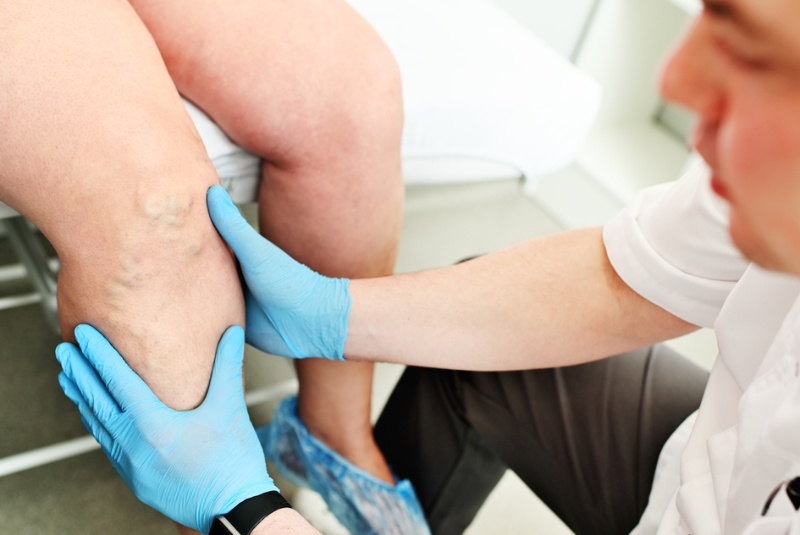
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Diagnosing lymphedema involves a comprehensive medical history review and a physical examination. Imaging tests like lymphoscintigraphy and MRI can provide detailed insights. Once diagnosed, healthcare professionals determine the stage and devise an appropriate management plan tailored to the patient's needs.
Management and Treatment
Lymphedema management focuses on reducing swelling, controlling pain, and improving overall quality of life. Treatment includes complete decongestive therapy (CDT), which involves manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), compression therapy, exercise, and skincare. Additionally, pneumatic compression devices and medications may be used to alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly impact lymphedema management. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good hygiene, avoiding constrictive clothing, protecting the skin from injuries, and following a balanced diet are essential measures. Physical activity and exercises prescribed by a healthcare professional can also aid in managing lymphedema.
Preventing and Minimizing Swelling
Preventive measures are crucial to minimize swelling and manage lymphedema effectively. These include regular skin care, elevation of affected limbs, use of compression garments, and appropriate exercises. Additionally, staying proactive in recognizing early signs of swelling and seeking prompt medical attention is vital.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Lymphedema can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on individuals. Coping with a chronic condition, body image concerns, and adapting to lifestyle changes can be challenging. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or therapists can help in managing these emotional aspects.
Conclusion: Managing Lymphedema Swelling
Lymphedema is a chronic condition that requires careful management to control and minimize swelling. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, early diagnosis, and following an appropriate treatment plan are key aspects of effective lymphedema management. By incorporating lifestyle modifications and preventive measures, individuals with lymphedema can improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of swelling.

