Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, poses significant challenges for many individuals worldwide. Characterized by persistent itching and red, inflamed skin, its symptoms can create both physical discomfort and emotional stress. Discover what atopic dermatitis really looks like, understand its root causes, and explore the array of treatment options available today to manage this chronic condition.
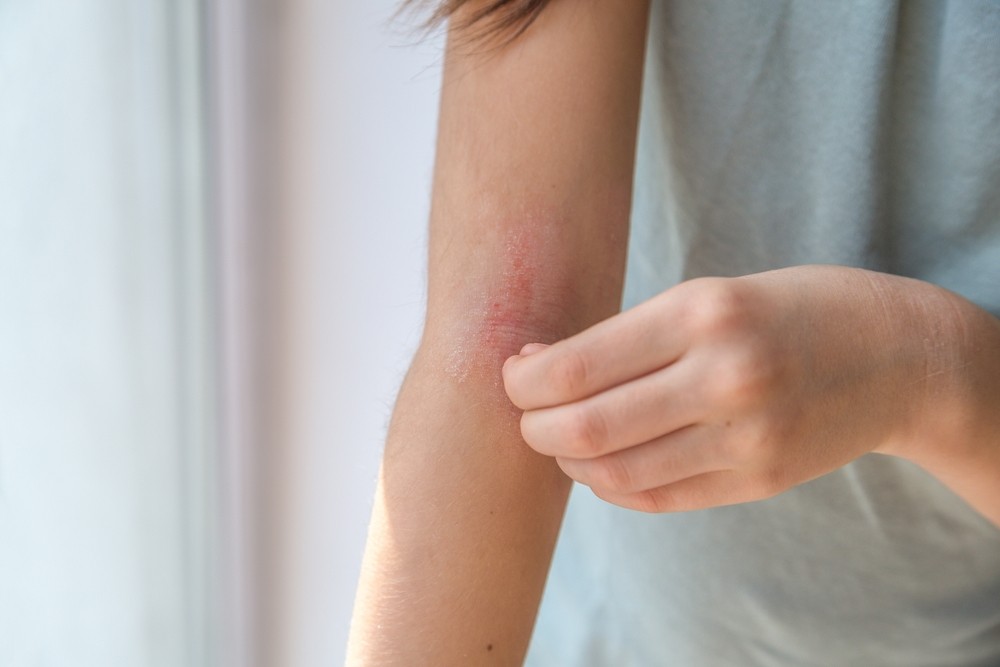
What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that typically develops in early childhood but can persist or reoccur throughout life. It is part of a group of conditions known as atopic, which also includes asthma and hay fever, indicating that they are connected with an overactive immune response to allergens. Learn more about this condition through the American Academy of Dermatology Association's overview of atopic dermatitis.
This skin disorder is characterized by dry, itchy skin that can appear red, inflamed, and cracked. It tends to flare periodically and then subside. Although atopic dermatitis is not life-threatening, its impact on quality of life is profound and often underestimated.
Signs and Symptoms
Understanding the signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis is crucial for early diagnosis and management. According to the Mayo Clinic, which provides detailed information on the condition's symptoms and causes here, the primary symptoms include:
- Itching: Often intense, itching is frequently the earliest sign, occurring even before the rash becomes visible.
- Red or brownish patches: Typically appearing on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and in the creases of the elbows and knees. Infants can also experience patches on the face and scalp.
- Small, raised bumps: These may ooze fluid when scratched and then crust over.
- Thickened, cracked, or scaly skin: This can develop over time, especially if the affected areas are scratched frequently.
- Raw, sensitive, swollen skin: These symptoms occur due to scratching-induced inflammation and skin barrier disruption.
For a more exhaustive list, this resource from the National Eczema Association provides additional insights into the diverse manifestations of atopic dermatitis.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis remains uncertain, but it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. According to Cleveland Clinic resources, several key risk factors have been identified:
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
- Immune System: An overactive immune response can trigger symptoms in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Environmental Triggers: Substances like tobacco smoke, harsh soaps, fabrics, and flying allergens can worsen the condition.
- Climate: Living in urban areas with higher pollution levels or in cold climates can increase the risk.
More details on causes and potential risk factors can be found through the information provided by NIAMS - Atopic Dermatitis Treatment, Symptoms & Causes.
Common Treatments
Various treatment strategies exist to manage atopic dermatitis, focusing on reducing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Here are some common approaches:
- Moisturizing: Regular and liberal use of moisturizers can help maintain skin hydration and protect the skin barrier.
- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments are often used to control inflammation and soothe itching.
- Wet Dressings: Applying wet wraps over areas with intense rashes can improve moisturization and absorption of topical treatments.
- Phototherapy: For severe cases, exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV rays can be effective.
For a comprehensive overview of treatment options, NIAMS provides an in-depth guide.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications and home remedies can play a crucial role in managing atopic dermatitis:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding individual triggers can prevent flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known exacerbator of eczema symptoms. Practices like yoga, meditation, and other relaxation techniques can be beneficial.
- Bathing Practices: Opting for lukewarm showers and using mild, fragrance-free cleansers can help mitigate symptoms.
- Dietary Considerations: In some cases, a diet free from common allergens (e.g., dairy, nuts, and seafood) can help in reducing outbreaks, but this should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
The National Eczema Association offers practical tips for managing eczema, including occupational and environmental adjustments, to better handle your symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of atopic dermatitis can be managed with over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle adjustments, it is essential to seek professional help when:
- Symptoms Are Severe: If you experience an extensive rash, intense discomfort, or if symptoms interfere significantly with everyday life.
- Infection Suspected: Signs include fever, swelling, pus, or a hot and painful rash.
- Home Care Isn't Effective: Persistent symptoms despite following self-care measures should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Recognizing these signs can ensure timely and appropriate interventions by healthcare professionals, offering better management outcomes and a better quality of life.
Atopic dermatitis can be a complex and challenging condition to manage, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can empower individuals to effectively navigate the condition and enhance their life quality. For further reading and detailed medical resources, please consult trusted sites such as the Cleveland Clinic or the Mayo Clinic.



